Skador relaterade till fotens belastning
Vid gång belastas foten med cirka 1–1,5 gånger kroppsvikten i varje steg. Vid löpning kan belastningen öka till mellan 4 och 6 gånger kroppsvikten. Små anatomiska avvikelser i foten kan därför få stora konsekvenser över en längre tid.
Belastning vid gång och löpning
Låga eller höga fotvalv, ökad eller minskad rörlighet i fotens leder samt otillräcklig muskelaktivitet i underbenet kan leda till felaktig belastning. Hos personer som går, joggar eller springer regelbundet kan detta ge upphov till smärta och skador.
En avvikande mekanik i foten påverkar linjeringen i hela den kinetiska kedjan och kan förändra belastningen i knä, höft, bäcken och rygg.
Fotens mekanik och överpronation
Överpronation är en av de vanligaste bakomliggande orsakerna till belastningsrelaterade besvär. Den uppstår ofta på grund av för stor rörlighet i subtalarleden, men även ökad rörlighet i midtarsalleden kan påverka fotens stabilitet, särskilt i slutet av stegets avveckling (framfotspronation).

Vanliga skador och besvär
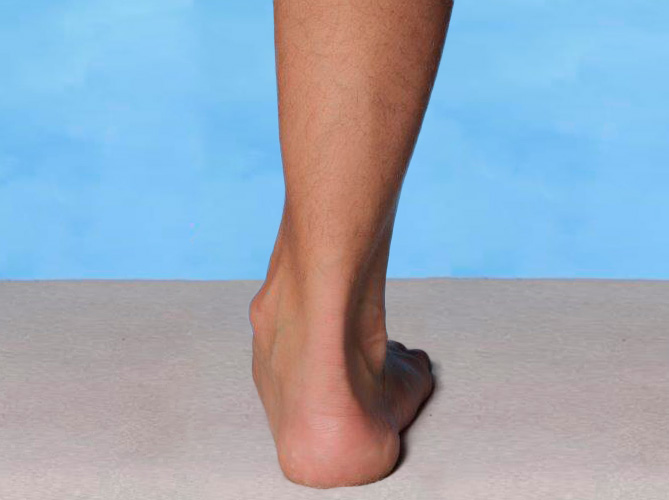
Pronation och överpronation
Pronation är en normal och nödvändig rörelse som gör att foten kan anpassa sig till ojämnt underlag och fungera som stötdämpare. Rörelsen innebär att det inre fotvalvet sänks under belastning.
Överpronation är däremot en för stor rörelse som kan påverka nästan alla leder i kroppen negativt och är en mycket vanlig orsak till överbelastningsskador.
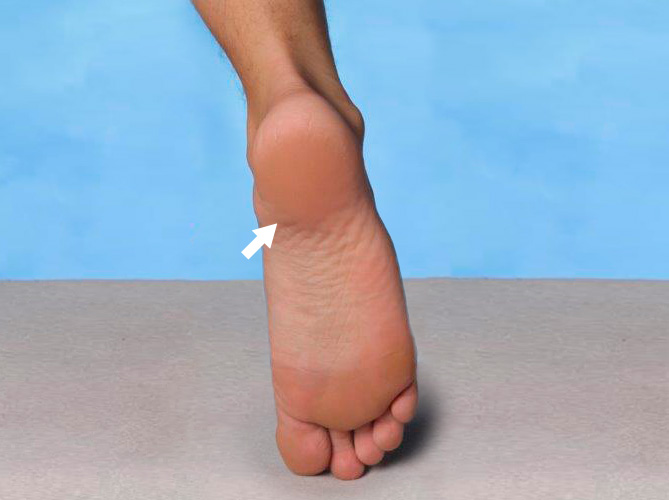
Hälsporre (plantar fasciit)
Plantar fasciit innebär en inflammation i plantarfascian och förekommer ofta hos personer med högt fotvalv (cavusfot). Typiska symtom är morgonsmärta och ömhet vid den inre främre delen av hälbenet.
Individuellt formade, stabiliserande inlägg som ger stöd under hela foten är ofta en effektiv åtgärd.
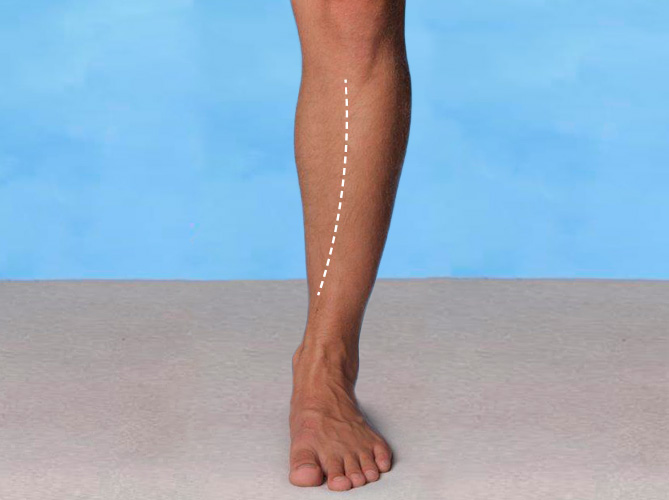
Benhinneproblem
Benhinneinflammation uppstår vanligtvis längs den inre kanten av skenbenet. Musklerna tibialis anterior och tibialis posterior blir överbelastade.
Vanliga orsaker är för snabb träningsprogression, byte av underlag samt överpronation. Ofta samverkar flera faktorer.
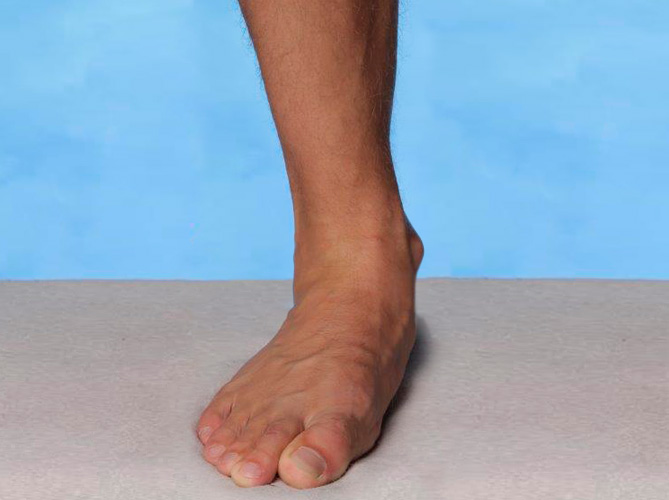
Hallux valgus
Hallux valgus är ofta relaterat till överpronation snarare än till smala skor. Tillståndet drabbar oftare kvinnor, vilket delvis kan förklaras av större generell ledrörlighet.
Stortån spelar en avgörande roll för fotens stabilitet i gångfasen. Vid uttalad hallux valgus försämras stabiliteten och smärta i stortåns grundled är vanligt.
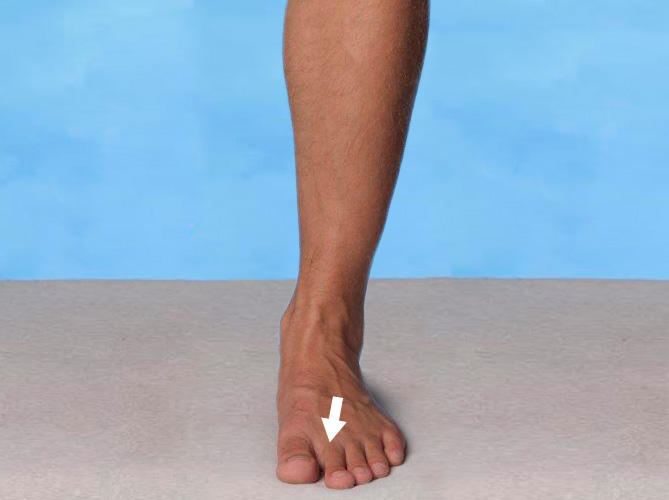
Mortons syndrom
Mortons syndrom uppstår ofta till följd av ett nedtrampat främre fotvalv. Överpronation gör att stortån pressar övriga tår utåt, vilket kan leda till inklämning av en nerv.
Smärtan uppstår främst vid belastning och kan ofta lindras med pelott samt ett inlägg som stödjer fotvalvet.
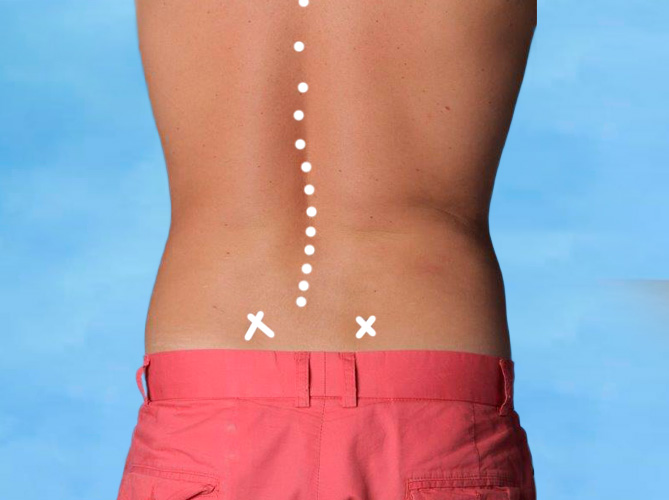
Ryggproblem
Felaktig fotmekanik kan bidra till att bäckenet hamnar i snedställning. Detta kan i sin tur påverka höftens position och leda till ryggbesvär.

Hälseneproblem
Hälseneproblem är vanligt förekommande, särskilt hos växande barn och idrottsaktiva. Vid överpronation ökar vinkeln på hälbenet, vilket förändrar belastningen på hälsenan i negativ riktning.
